The Transformative Power of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the landscape and texture of almost every field or sector. From self-driving automobiles to precision medicine, AI technologies’ domains are countless and expanding fast. This article describes AI, discusses its uses, and touches upon the ethical difficulties and implications of its integration into everyday life.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
AI is the replication of the human mind and its functionalities in machines capable of processing information in the same manner as the human brain. Artificial intelligence is the simulation of the human logical and intelligent behavioral process with the help of special computer programs, aimed to reproduce human thinking and logic while realizing tasks that include speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. These systems employ specific calculations and probability theories to feed on data, learn from it, and draw decisions.
There are two main types of AI: narrow AI and general AI. Narrow AI, also called weak AI, is created to perform a particular task or several particular tasks, such as face recognition or web search. General AI, or strong AI, is an advanced AI that can solve any intellectual problem that a human can solve. Thus, while narrow AI is already in use, general AI is still mostly a concept.

Key Components of AI
AI comprises several key components, each contributing to its ability to learn and make decisions:
- Machine Learning (ML): The branch of AI where algorithms are given data to learn and then make predictions or decisions from the learned data. Their performance increases with data exposure, proposing that machine learning algorithms can be learned from the inputs. Get to know more about machine learning.
- Computer Vision: This field enables one to train a machine to understand images and make judgments or conclusions about them. Some use cases are Face identification, Self-driving cars, and Medical image analysis. See more on computer vision.
- Neural Networks: Defined by the human brain, new neural networks are several algorithms that try to identify patterns in a given dataset. They are most effective in the processes related to image or speech recognition. Take more time to learn about neural networks.

- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This component creates a machine that can interpret and answer issues in natural language. Some of the primarily implemented areas of NLP include chatbot services, language translation services, and voice assistant systems. Learn more about NLP.
Applications of AI
AI’s impact is evident across various sectors, transforming industries and enhancing efficiencies:
- Healthcare: AI disrupts healthcare through precision medicine, diagnostic outcomes, and disease prediction. For instance, with the help of AI algorithms, it is possible to recognize diseases like cancer at earlier stages with considerably higher effectiveness than it can be done with human assistance. Explore AI in healthcare.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars are among the most convincingly promising use examples of developed AI. They use computer vision, machine learning, and several artificial intelligence techniques for safe and efficient road usage of self-driving cars.

- Finance: AI is employed in financial services to address fraud and trade and offer financial advice. Machine learning models can extract patterns from transactions so that they can detect fraudulent activities in the future. Understand what AI finance is.
- Education: Smart technologies offer opportunities for differentiated learning. The applications understand everyone is learning styles and help teachers determine when students require extra assistance. Explore AI in education.
- Retail: This is achieved through recommenders offering AI solutions for customer preferences, chatbots for efficiently handling customer issues, and inventory controls for product management. AI, along with tools like an AI video generator, enables retailers to forecast customer behavior and patterns, helping them manage stock and inventory well in advance to avoid huge waste while visually presenting predictive trends. Discover AI in retail.

Figure 1: Artificial Intelligence in eCommerce & Retail
Ethical Considerations
Despite AI’s positive impacts on various aspects of people’s lives, it brings critical questions of ethics. These include:
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can continue to reproduce the bias found in datasets that they have been trained with. Bias in models is another daunting task in the development of AI, where equity has to be maintained constantly. Learn about AI bias.
- Job Displacement: As AI takes over more jobs and activities, there is apprehension about its effects on employment. Some general tips to consider when managing such an outcome include how the impact on workers might be lessened and how they can transition into new forms of work that require training. Acquaintance with AI and job displacement.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: New questions on responsibility and trust arise when such essential parts of people’s lives as healthcare and automobiles are based on AI. Something that is required is the definition of clear rules and regulations on how to use AI safely or ethically. Click to learn more about ethical issues with AI.
- Privacy: AI solutions entail handling vast volumes of personal data, which may harm citizens’ data protection. The User data, particularly their identity, should be protected, and there should be clarity on how it will be utilized. Look at AI and privacy and get more information on it.
The Future of AI
AI has a bright future. As technology grows, one is likely to find even more uses and breakthrough inventions in the future. AI can solve many global issues humans face today, including climate change and international health. Nevertheless, attaining this indicates a need to address ethical concerns and a dedication to AI’s advancement that can benefit everyone in society.
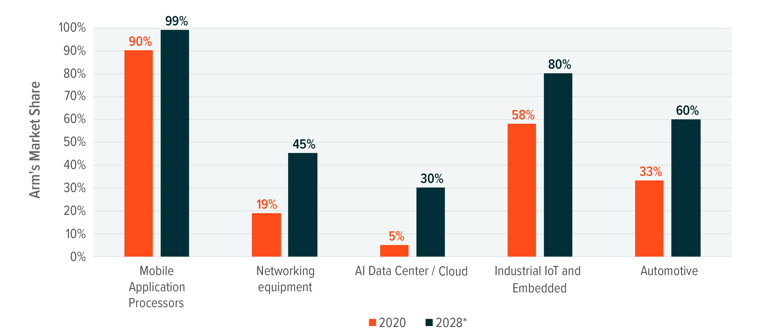
Figure 2: Artificial Intelligence and Profitability Efforts
Thus, AI is a progressive technology that is currently changing different aspects of human life. Learning about the constituents’ uses and ideas arising from AI can help manage advantages and disadvantages. Thus, to go further, it is essential to develop and implement AI as constructively as possible, which means using the opportunities in people’s best interest.
Article by Aqsa Pandith






